Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Airfoil in open jet – steering vectors.#
Demonstrates different steering vectors in Acoular and CSM diagonal removal. Uses measured data in file example_data.h5, calibration in file example_calib.xml, microphone geometry in array_56.xml (part of Acoular).
from pathlib import Path
import acoular as ac
from acoular.tools.helpers import get_data_file
The 4 kHz third-octave band is used for the example.
Obtain necessary data
time_data_file = get_data_file('example_data.h5')
calib_file = get_data_file('example_calib.xml')
First, we define the time samples using the MaskedTimeSamples class that
provides masking of channels and samples. Here, we exclude the channels with index 1 and 7 and
only process the first 16000 samples of the time signals. Alternatively, we could use the
TimeSamples class that provides no masking at all.
t1 = ac.MaskedTimeSamples(file=time_data_file)
t1.start = 0
t1.stop = 16000
invalid = [1, 7]
t1.invalid_channels = invalid
Calibration is usually needed and can be set as a separate processing block with the
Calib object. Invalid channels can be set here as well, by setting the
invalid_channels attribute.
calib = ac.Calib(source=t1, file=calib_file, invalid_channels=invalid)
The microphone geometry must have the same number of valid channels as the
MaskedTimeSamples object has. It also must be defined, which channels
are invalid.
micgeofile = Path(ac.__file__).parent / 'xml' / 'array_56.xml'
m = ac.MicGeom(file=micgeofile)
m.invalid_channels = invalid
Next, we define a planar rectangular grid for calculating the beamforming map (the example grid is
very coarse for computational efficiency). A 3D grid is also available via the
RectGrid3D class.
g = ac.RectGrid(x_min=-0.6, x_max=-0.0, y_min=-0.3, y_max=0.3, z=-0.68, increment=0.05)
For frequency domain methods, PowerSpectra provides the cross spectral
matrix (and its eigenvalues and eigenvectors). Here, we use the Welch’s method with a block size
of 128 samples, Hanning window and 50% overlap.
f = ac.PowerSpectra(source=calib, window='Hanning', overlap='50%', block_size=128)
To define the measurement environment, i.e. medium characteristics, the
Environment class is used. (in this case, only the speed of sound
is set)
env = ac.Environment(c=346.04)
The SteeringVector class provides the standard freefield sound
propagation model in the steering vectors.
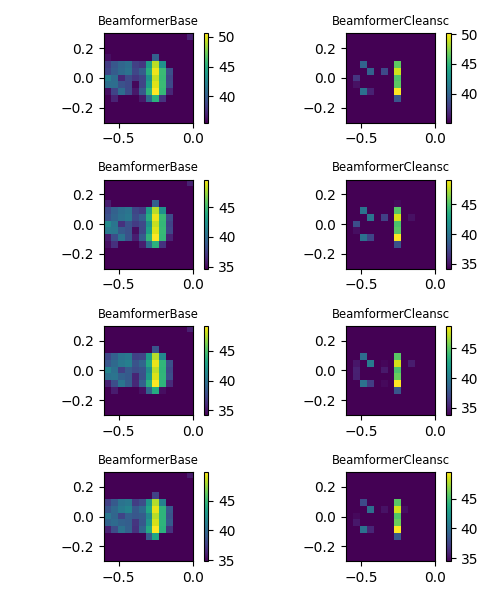
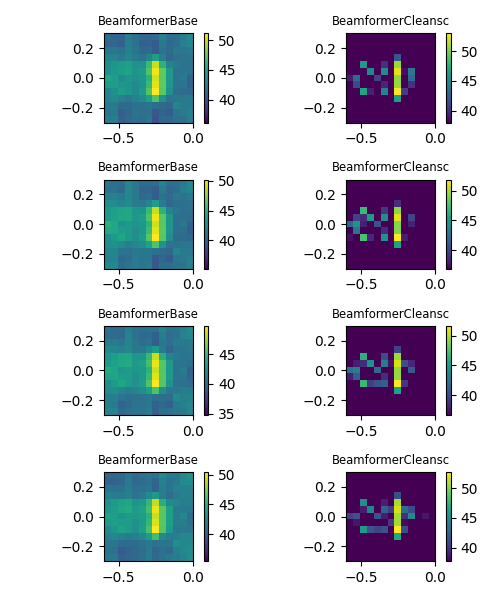
Finally, we define two different beamformers and subsequently calculate the maps for different
steering vector formulations. Diagonal removal for the CSM can be performed via the
r_diag parameter.
Plot result maps for different beamformers in frequency domain (left: with diagonal removal, right: without diagonal removal).
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fi = 1 # no of figure
for r_diag in (True, False):
plt.figure(fi, (5, 6))
fi += 1
i1 = 1 # no of subplot
for steer in ('true level', 'true location', 'classic', 'inverse'):
st.steer_type = steer
for b in (bb, bs):
plt.subplot(4, 2, i1)
i1 += 1
b.r_diag = r_diag
map = b.synthetic(cfreq, num)
mx = ac.L_p(map.max())
plt.imshow(ac.L_p(map.T), vmax=mx, vmin=mx - 15, origin='lower', interpolation='nearest', extent=g.extent)
plt.colorbar()
plt.title(b.__class__.__name__, fontsize='small')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
[('example_data_cache.h5', 3)]
[('example_data_cache.h5', 4)]
[('example_data_cache.h5', 5)]
See also
Airfoil in open jet – Frequency domain beamforming methods. for an application of further frequency domain methods on the same data.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.146 seconds)